If you’re curious how brands get their websites to rank at the top of the search engine results page (SERP) adorned with that little “Sponsored” tag above the listings, then you’ve come to the right place.
Even in the midst of an AI renaissance, billions of people are still searching for solutions on Google. And as long as people are searching, there will always be a place for SEO and paid search ads (also known as PPC ads).
Brands looking to amplify their exposure on search engines can purchase paid search ad placements primarily through Google Ads and Microsoft Ads. This article is meant to break down the complexities of paid search ads so you can understand how they work and how they can benefit your business.
We’ll explore everything from the basic principles of paid search to the latest automated strategies that are transforming the way businesses purchase digital ads. Whether you’re a newcomer starting out or a seasoned marketer refining your approach, this guide helps you navigate the world of paid search marketing.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
What is Paid Search Marketing?
Paid search marketing is a form of digital paid media that places your ads in front of users who are actively searching for products, services, or solutions similar to what your business offers. These ads appear on search engine results pages (SERPs), often above organic results, giving advertisers an opportunity to attract highly engaged potential customers.
Unlike display advertising, paid search ads are primarily text-based, while display ads are image-based and appear on websites within Google’s ad network.
Search ads are also usually paid for by the click, which is where we get the term “pay-per-click” advertising or “PPC.” The other term used for this is “CPC” which stands for “cost-per-click.” In contrast, Display advertising is usually paid for on a CPM basis, which stands for “cost-per-mille” (per 1,000 impressions).

Although display ads are often strategized and purchased alongside search ads, they are handled completely differently. That’s why this article will focus on search ads specifically.
As of writing this, automated strategies continue to supplant traditional methods like manual keyword targeting or static ad copy. Moving toward automation makes paid search a more efficient way to reach relevant audiences, using data-driven decision-making to determine which ads are shown, how they’re placed, and who sees them.
However, there comes with automation its own set of challenges that still require a strategic and careful hand to extract positive ROI from paid search ads (more on this later).
For now, let’s run through some of the main benefits of paid search ads.
The Benefits of Paid Search Marketing
Compared to SEO, which involves ranking a website on search engines in organic ways, paid search marketing provides numerous advantages that help businesses achieve their goals efficiently — for a cost, of course. While organic search results take time and effort to achieve, they offer longstanding, cost-effective traffic compared to paid search ads:
- Immediate visibility: Ads appear quickly, often at the top of SERPs, making it easy to capture attention.
- Precise audience targeting: Ads can be fine-tuned to specific demographics and interests, enhancing relevance.
- Cost-effectiveness: Paid search allows for controlled spending, with the ability to set daily budgets and maximum bids.
- Scalability: As campaigns succeed, it’s easy to scale up budgets, targeting, and ad variations to expand reach.
- Measurable results: Performance metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS) offer real-time insights to guide future optimization efforts.
Paid search campaigns also provide more direct control over ad visibility compared to organic listings. In many cases, paid ads can even outrank organic results and SERP features, ensuring your brand is seen first when users search for relevant queries.
You might be asking, “can’t SEO accomplish the same results without having to spend money on ads?” That is completely accurate, but SEO takes time to percolate in search engines.
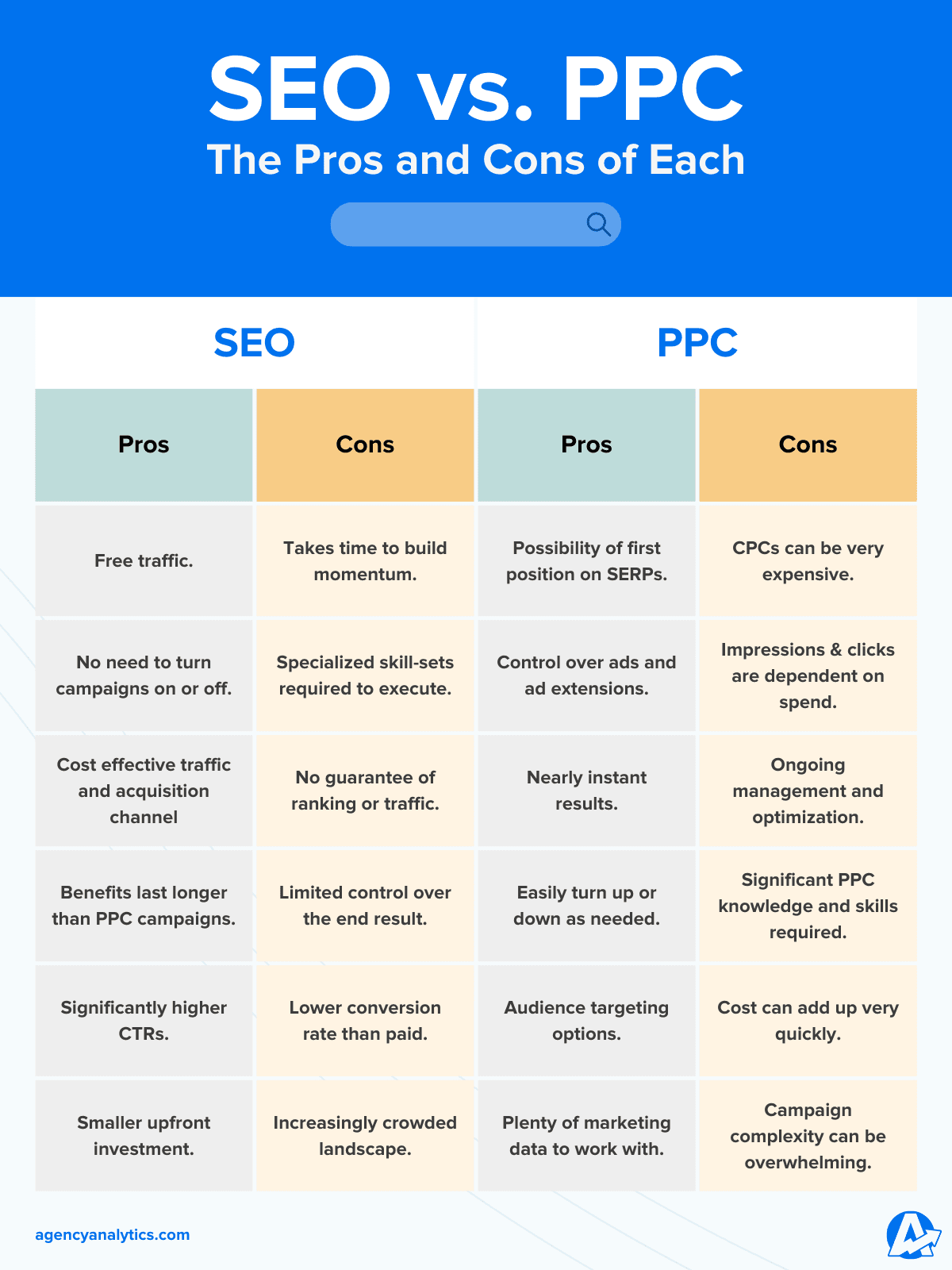
Image Source: Agency Analytics
Setting Up a Paid Search Campaign
The first step in managing your paid search campaigns is setting up a Google Ads or Microsoft Ads account. Carefully consider these elements to make sure your campaign reaches the right audience and achieves its objectives.
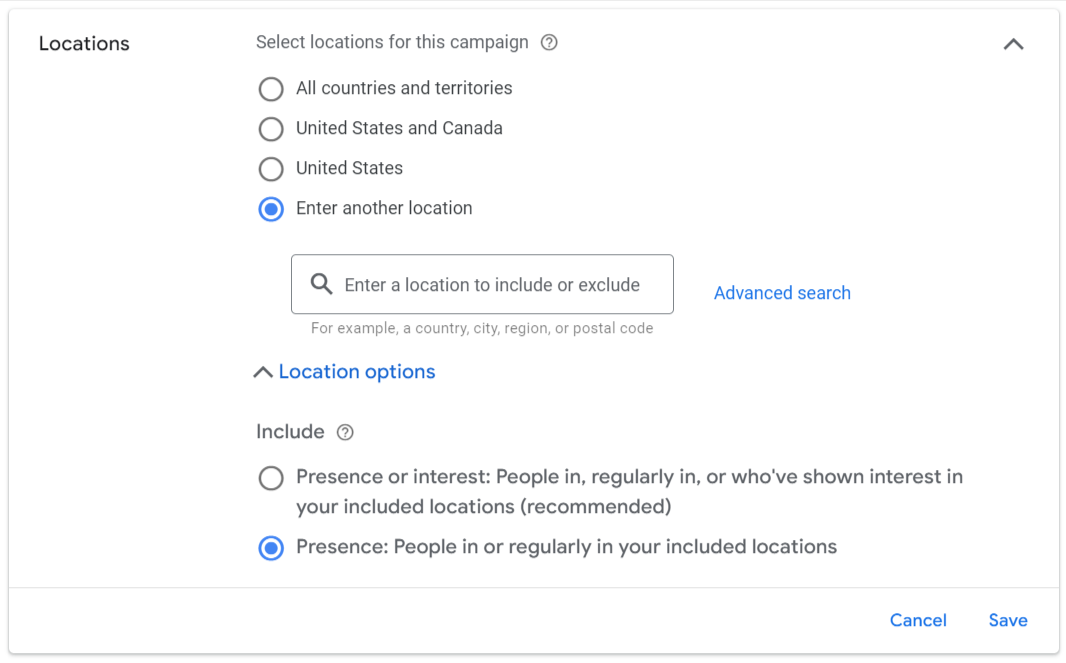
Location Settings
Choosing where your ads go is crucial for targeting the right audience. Location settings allow you to specify countries, regions, zip codes, or cities where your ads will appear.
For example, if you run a local business, targeting users within your city or state directs your ad budget toward prospects likely to convert.
Keyword Strategy
While keyword selection remains a core part of search advertising, the role of manual keyword management has diminished as automation becomes more prevalent.
Google’s shift towards broad match terms means advertisers can rely more on the algorithm to match ads to a wider variety of relevant searches rather than focusing solely on exact or phrase matches. Broad match allows Google Ads to take user intent into account, displaying ads for queries that might not exactly match your keywords but are contextually relevant.
However, using broad match does come with the risk of irrelevant clicks, which is why a robust negative keyword list is essential.
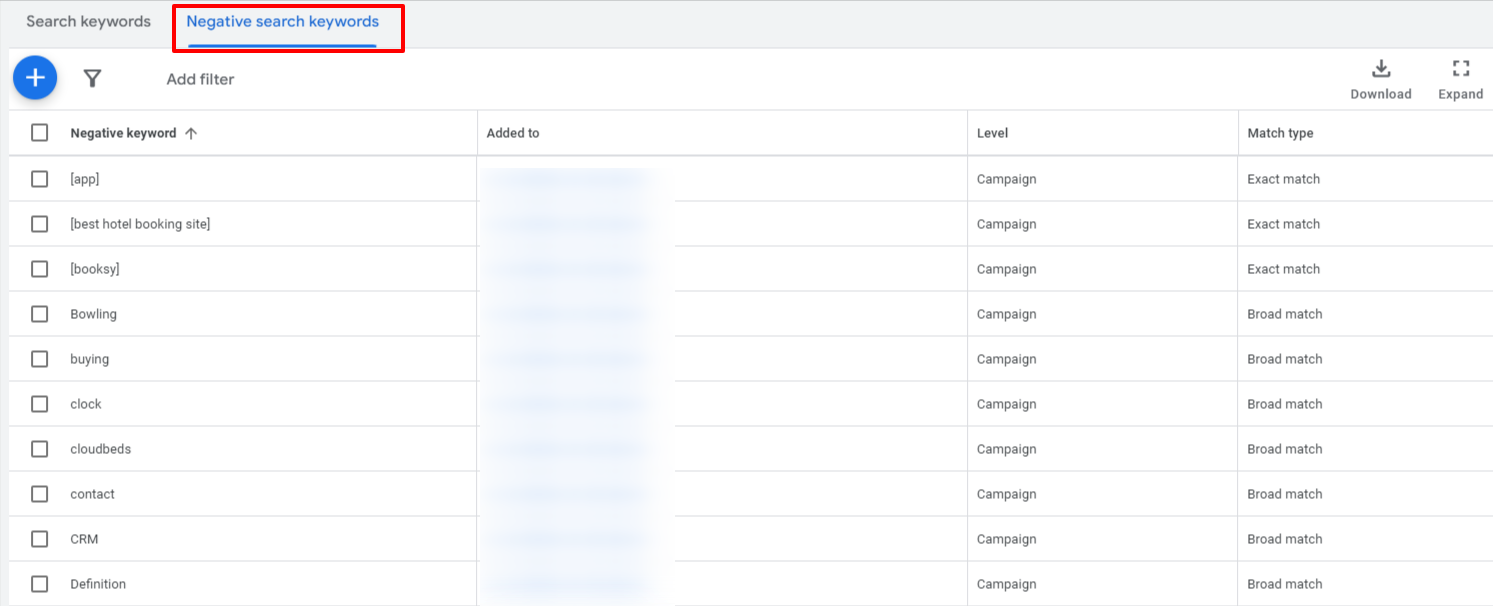
Negative keywords prevent your ads from appearing in searches that don’t align with your goals, ensuring your budget isn’t wasted on irrelevant traffic. For example, a company selling premium fitness equipment may want to exclude terms like “free” or “cheap” to avoid users who aren’t looking to make a purchase.
Ad Creation
Creating effective ads requires an understanding of both your audience and your competition. Dynamic search ads (DSAs) and responsive search ads (RSAs) play a significant role in paid search marketing. Instead of manually crafting static ads for every keyword or product, DSAs use your website’s content to automatically generate ads that match the searcher’s intent. RSAs pull several pieces of ad copy from a pool of options you provide, working together to deliver the most relevant solution based on the user’s query.
To enhance the relevance of your ads, make use of:
- Engaging ad copy: The headline should capture attention, and the body copy must align with the user’s search intent.
- Call-to-action (CTA): Include a clear and concise CTA that prompts users to take the next step, such as “Shop Now” or “Learn More.”
- Ad extensions: Enhance your ads by including additional information like location, phone numbers, or specific product offerings. These extensions provide more context and can improve click-through rates.
Choosing Your Bid Strategy
Determining how much you’re willing to spend on each click and setting a budget are vital aspects of paid search marketing. Much of optimizing the way you pay for PPC ads comes with choosing the right bidding strategy to meet your advertising goals. Here’s a quick rundown on the types of bidding strategies currently available in Google Ads:
- Maximize Clicks (Automated): Automatically adjusts bids to get as many clicks as possible within your budget.
- Maximize Conversions (Automated): Focuses on optimizing bids to drive the most conversions based on your campaign goals.
- Target Impression Share (Automated): Aims to get your ads in front of a certain percentage of searchers for better visibility.
- Enhanced Cost Per Click or ECPC (Semi-Automated): Tweaks your manual bids to boost conversions while keeping some control over costs.
- Target ROAS (Automated): Adjusts bids to help you achieve a specific return on ad spend, aiming for maximum conversion value.
- Manual CPC (Manual): You set bids yourself for each keyword or ad group, giving you full control over your budget.
- Target CPA (Automated): Automatically adjusts bids to achieve conversions at your target cost per acquisition.
- Cost Per View or CPV (Automated): Charges apply each time someone watches your video ad, commonly used for video campaigns.
- Target CPA (Automated): Similar to the first, it focuses on driving conversions at your target cost per action.
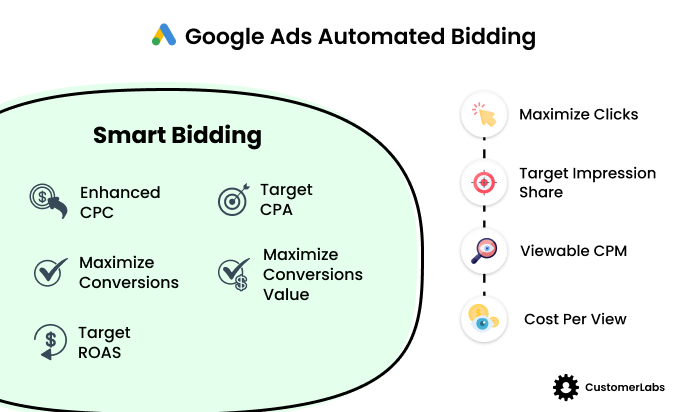
Image Source: CustomerLabs
As you can see, most of these are automated, and that’s by design. If you were going to run ads in the 2010-2020 era of Google Ads (formerly “Google AdWords” at the time), then practically all of these would still be manual bidding strategies. That, however, is no longer the case.
Traditional manual bidding strategies are increasingly giving way to these automated bidding strategies. Tools like Google’s Smart Bidding optimize your bids in real time by using machine learning to adjust for the likelihood of conversion, user context, and competitive factors.
For instance, with strategies like Target CPA (cost per acquisition) or Maximize Conversions, Google can automatically manage your bids based on your campaign goals. This automation reduces the need for constant manual adjustments and improves efficiency.
- Bid: This is the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for a click on your ad. Higher bids increase your chances of ranking at the top, but effective ad copy and relevance can improve positioning even at lower bids.
- Quality Score: Google Ads calculates Quality Score based on expected click-through rate, ad relevance, and landing page experience. Higher scores lead to better ad positions and can lower the cost per click, making this a critical factor in your campaign’s success.

Image Source: Search Engine Land
Creating Effective Paid Search Ads
To create ads that resonate with your target audience and convert efficiently:
- Focus on relevance: Ensure your ads closely align with the search intent behind user queries.
- Continuously refine your campaigns: Regularly review performance data to optimize ad copy, targeting, and bidding strategies.
- Use automation tools: Automation not only saves time but also allows you to scale your efforts without sacrificing precision. It’s still wise (and encouraged) to scan through all of the ad copy and landing pages derived by AI to ensure accuracy and brand tone.
- Make use of ad extensions: Extensions can show extra information, such as links to specific pages on your website, customer reviews, or product prices, providing more value to potential customers.
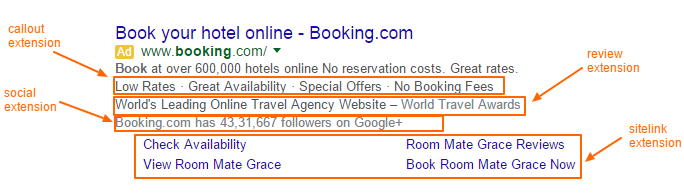
- Scale your campaigns when you’re ready: Start small, focusing on specific products or services, and gradually scale as you gather data and refine your strategy. Automation tools can help streamline this process.
- Measure success: Focus on key metrics like CPC, CPA, and ROAS to track and optimize your PPC performance. Use this data to adjust your strategy and ensure you’re getting the best return on your ad spend.
Let’s Start Advertising
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Paid Search
While automation can greatly enhance the efficiency of paid search campaigns, it’s not without its challenges. Relying too heavily on automated processes without proper oversight can lead to costly mistakes. Here are the common pitfalls in paid search marketing and how to avoid them.
1. Relying Too Heavily on Broad Match Keywords Without Monitoring Them
Broad match keywords allow your ads to show up for a wide range of searches, potentially reaching a broader audience. However, without a well-maintained negative keyword list, broad match can show your ads for irrelevant search terms, leading to wasted ad spend on clicks that don’t convert.
2. Focusing on Activities Over Outcomes
It’s easy to get caught up in campaign setup—creating ad groups, selecting keyword phrases, and setting bid strategies. But the real focus should always be on driving conversions. Automated tools like Maximize Conversions or manual CPC bidding can be helpful, but if you aren’t monitoring how well your ads are meeting your conversion goals, you risk spending more without seeing returns.
Ensure every aspect of your paid search campaign aligns with broader business objectives, whether it’s driving traffic to a PPC-optimized landing page, generating leads, or increasing sales through Google Shopping ads. Automation can handle the mechanics, but human oversight is necessary to measure performance metrics like return on ad spend (ROAS) and make sure you’re meeting the right outcomes.
3. Failing to Forecast Results Before Scaling Up
One of the biggest mistakes in paid search advertising is scaling up your campaign before properly forecasting results. Automated bidding strategies make it easy to increase your spend, but they don’t account for external factors like market fluctuations or competitor activity. Using tools like Google Keyword Planner or forecasting methods allows you to predict campaign performance based on metrics such as cost per click (CPC), competition, and keyword demand.
Don’t rely solely on automation when expanding your budget. Before you increase your spend, review historical data and run forecasts to ensure your campaign is scalable and likely to be profitable.
Balancing Automation with Human Expertise
Automation has revolutionized search engine marketing, but a completely hands-off approach can backfire. While automation is crucial for paid search, search engine optimization (SEO) remains essential for attracting organic traffic. Human oversight remains essential for optimizing campaigns, even when using the most advanced automation tools.
- Align your ad copy with relevant landing pages: Automation can manage bids, but it can’t craft compelling ad copy or optimize landing pages for conversions. Humans play a key role in ensuring ad messaging resonates with your audience and that users have a seamless experience when they click through to your site.

Image Source: Optimize Press
- Monitor and adjust your campaign’s bidding strategy if necessary: While automated bidding strategies adjust in real-time, they can miss important shifts in user behavior or competitive trends. A human manager can step in to tweak keyword phrases, ad placements, and bid strategies to keep your campaign optimized as conditions change.
- Stay focused on outcomes: Automation manages tasks well, but humans align campaigns with long-term business objectives. Focusing on conversion rates, ad rank, and overall campaign performance prevents you from getting bogged down in campaign setup and optimization activities.
Last Words on Paid Search Marketing
Paid search marketing continues to evolve as automated bidding strategies and dynamic search ads take center stage. These technologies offer efficiency and scalability that traditional methods struggle to match, allowing businesses to drive targeted traffic and increase conversions while maintaining tight control over their budgets.
With careful attention to things like negative keywords and automated features, you can optimize your search campaigns for maximum impact in a highly competitive ad space.
If you’re ready to level up your brand’s paid search marketing, Single Grain’s paid media experts can help!👇
Let’s Start Advertising
Paid Search Marketing Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is paid search marketing?
Paid search marketing is a form of online advertising where businesses bid on keyword phrases to have their ads appear on search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google search results. These ads, also known as PPC (pay-per-click) ads, are displayed above or alongside organic search results.
-
How does paid search advertising differ from SEO?
Paid search advertising involves paying for ad placement on search engines, while search engine optimization (SEO) focuses on improving your website’s organic ranking. Paid search ads appear immediately, while SEO takes time to rank in search results.
-
What platforms can I use for paid search advertising?
Google Ads and Microsoft Advertising are the two major search engines for paid search ads.
-
How are paid search ads ranked?
Paid search ads are ranked based on ad rank, which is determined by your maximum bid and Quality Score. Quality Score is influenced by factors like ad relevance, expected click-through rate (CTR), and the quality of your landing page.
-
What are negative keywords in paid search campaigns?
Negative keywords are search terms you exclude from triggering your ad. Using a robust negative keyword list helps ensure your ads don’t appear in irrelevant searches, improving ad placement and optimizing your budget.
-
What is the difference between manual bidding and automated bidding?
Manual bidding allows you to set your CPC manually for each keyword, while automated bidding strategies, like Maximize Conversions or Target CPA, adjust bids in real-time using data and machine learning to optimize performance.
If you were unable to find the answer you’ve been looking for, do not hesitate to get in touch and ask us directly.
Related Video
For more insights and lessons about marketing, check out our Marketing School podcast on YouTube.
https://www.singlegrain.com/paid-media/paid-search-marketing/”>
#Paid #Search #Marketing #Work

